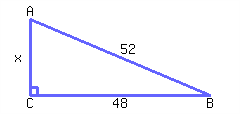
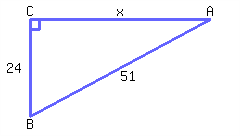
Example 7.5.1. Solving Quadratic Equations Using the Square Root Property.
Solve for \(w\) in \(3(2-w)^2-24=0\text{.}\)
Explanation.
It’s important here to suppress any urge you may have to expand the squared binomial. We begin by isolating the squared expression.
\begin{align*}
3(2-w)^2-24\amp=0\\
3(2-w)^2\amp=24\\
(2-w)^2\amp=8
\end{align*}
Now that we have the squared expression isolated, we can use the square root property.
\begin{align*}
2-w\amp=-\sqrt{8}\amp\text{or}\amp\amp2-w\amp=\sqrt{8}\\
2-w\amp=-\sqrt{\highlight{4}\cdot2}\amp\text{or}\amp\amp2-w\amp=\sqrt{\highlight{4}\cdot2}\\
2-w\amp=-\sqrt{\highlight{4}}\cdot\sqrt{2}\amp\text{or}\amp\amp2-w\amp=\sqrt{\highlight{4}}\cdot\sqrt{2}\\
2-w\amp=-\highlight{2}\sqrt{2}\amp\text{or}\amp\amp2-w\amp=\highlight{2}\sqrt{2}\\
-w\amp=-2\sqrt{2}-2\amp\text{or}\amp\amp-w\amp=2\sqrt{2}-2\\
w\amp=2\sqrt{2}+2\amp\text{or}\amp\amp w\amp=-2\sqrt{2}+2
\end{align*}
The solution set is \(\left\{2\sqrt{2}+2,-2\sqrt{2}+2\right\}\text{.}\)