Principle 5.8.2. EFFECTIVE DESIGN: Code Reuse.
Often the best way to solve a programming task is to find the appropriate methods in the Java class library.
java.text.NumberFormat
Math.round() method is useful for rounding numbers, it is not suitable for business applications. Even for rounded values, Java will drop trailing zeroes. So a value such as $10,000.00 would be output as $10000.0. This wouldn’t be acceptable for a business report.
java.text.NumberFormat class precisely for the task of representing numbers as dollar amounts, percentages, and other formats (Figure 5.8.1).
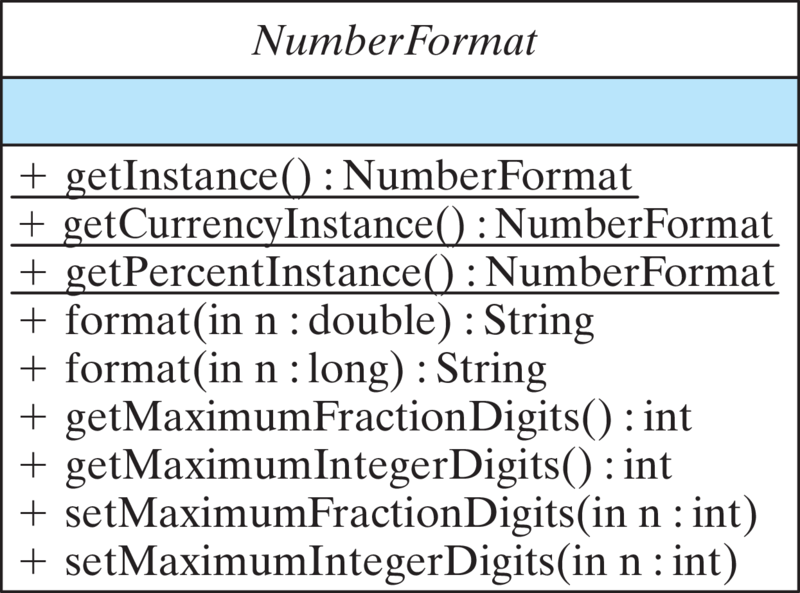
NumberFormat class.NumberFormat class is an abstract class, which means that it cannot be directly instantiated. Instead, you would use its static getInstance() methods to create an instance that can then be used for the desired formatting tasks.
NumberFormat instance has been created, its format() method can be used to put a number into a particular format. The setMaximumFractionDigits() and setMaximumIntegerDigits() methods can be used to control the number of digits before and after the decimal point.
NumberFormat dollars = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance();
System.out.println(dollars.format(10962.555));
NumberFormat percent = NumberFormat.getPercentInstance();
percent.setMaximumFractionDigits(2);
System.out.println(percent.format(6.55));
Math and NumberFormat classes illustrates the following principle:
| \(a = p(1 + r)^n\) where |
| \(\bullet\) a is the CD’s value at the end of the nth year |
| \(\bullet\) p is the principal or original investment amount |
| \(\bullet\) r is the annual interest rate |
| \(\bullet\) n is the number of years or the compounding period |
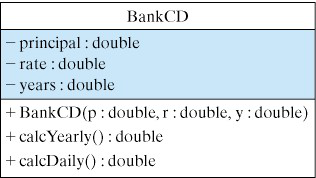
BankCD class.BankCD class that calculates the maturity value of a CD. Figure 5.8.4 gives the design of the class. It should have three instance variables for the CD’s principal, rate, and years. Its constructor method sets the initial values of these variables when a BankCD is instantiated. Its two public methods calcYearly() and calcMonthly() calculate and return the maturity value using yearly and daily compounding interest, respectively. Use the Math.pow() method to calculate maturity values. For example, the following expression calculates maturity value with annual compounding: principal * Math.pow(1 + rate, years)
BankCD class that lets the user input principal, interest rate, and years, and reports the CD’s maturity value with both yearly and daily compounding. Use NumberFormat objects to display percentages and dollar figures in an appropriate format. The program’s output should look something like the following (user’s inputs follow the ’>’ prompt):************************ OUTPUT ******************** Compare daily and annual compounding for a Bank CD. Input CD initial principal, e.g. 1000.55 > 2500 Input CD interest rate, e.g. 6.5 > 7.8 Input the number of years to maturity, e.g., 10.5 > 5 For Principal = 2,500.00 Rate= 7.8% Years= 5.0 The maturity value compounded yearly is 3,639.43 The maturity value compounded daily is: $3,692.30 ************************ OUTPUT ********************