
3.3. Representing Images¶
This lesson reinforces two important enduring understandings. First, a variety of abstractions built upon binary sequences can be used to represent all digital data. In this lesson, students see how digital sequences can be used to represent images. And, second, there are always trade-offs when representing information as digital data. In this lesson, we explore trade-offs that occur when compressing images: lossy compression algorithms trade the loss of some bits from the image in order to get higher levels of compression.
Professional Development
Complete the activities for Unit 3 Lesson 3.3: Representing Images.
Materials
- Projection system
- Printed copies of the Image Representation Activity worksheet (adapted from CS Unplugged)
- Image Compression Text Version
- Slides
3.3.1. Learning Activities¶
Estimated Length: 90 minutes
- Hook/Motivation (10 minutes): Ask students to think about how images are represented on computers. Look at a zoomed in image to see the pixels (example at http://introcomputing.org/image-1-introduction.html). If no one mentions it, explain computers break down images
into pixels, and that the term pixel is short for "picture element." Discuss image representation with the class, being sure to cover the following points:
- After breaking an image into pixels, computers use a variety of methods to represent each pixel or groups of pixels as numbers.
- Numbers are translated to bits, which are stored and sent like any other data.
- Other computers use the bits to reconstruct image.
- Storing specific information about every single bit would be an enormous amount of data for an image. What are some ways a computer might store an image using less data? Compression techniques!
- Experiences and Exploration (70 minutes):
- Have students watch the CS Unplugged video on image compression for a quick look at one way that images are represented and compressed.
- Do the RLE compression for the letter a below as a class or in pairs (the first row is 1, 3, 1). Draw it in on the board or in the interactive pixel grid under Practice in the student side or copy the image to a projected document.
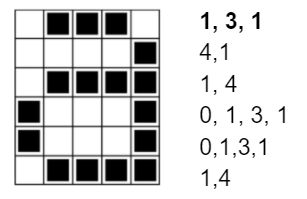
- Have students work in POGIL groups or pairs to complete the Image Representation worksheet. They could do these on paper or using the interactive pixel grid under Practice on the student side.
- Talk about how color is represented using RGB values, RGB Color explorer
When finished, present a more detailed explanation of run-length encoding, storing images on computers, and other image compression techniques. Mention the trade-off in compression which is quality vs. file size and lossy vs. lossless compression (whether some data is lost when compressing, see this additional resource on lossy vs. lossless compression). There are several ways you can present this information. If you are new to teaching Mobile CSP, we suggest starting by having students watch the video lecture. As you become more familiar with the lesson and its content, you may decide to use the slides to give the lecture on your own, or guide students through reading the text-based lesson.
- Have students watch the video of the Mobile CSP version of the lecture
- Use the slides to give the lecture yourself.
- Have students read the text-based version of the lesson.
- Optional Activities: If you have extra time, have students complete some of the "Other Activities" on the student side and watch some of the Still Curious videos (e.g.How Snapchat Filters work).
- Rethink, Reflect, and/or Revise (10 minutes): Have students complete the first two questions of their portfolio reflections in class and tell them to complete the last question for homework.
AP Classroom
The College Board's AP Classroom provides a question bank and Topic Questions. You may create a formative assessment quiz in AP Classroom, assign the quiz (a set of questions), and then review the results in class to identify and address any student misunderstandings.The following are suggested topic questions that you could assign once students have completed this lesson.
Suggested Topic Questions:
- Topic 2.2 Data Compression
Assessment Opportunities and Solutions
Solutions Note: Solutions are only available to verified educators who have joined the Teaching Mobile CSP Google group/forum in Unit 1.
Assessment Opportunities
You can examine students’ work on the interactive exercise and their reflection portfolio entries to assess their progress on the following learning objectives. If students are able to do what is listed there, they are ready to move on to the next lesson.
- Interactive Exercises:
Students should be able to use RLE to translate the numbers to images of letters in exercises 1 and 2. - Portfolio Reflections:
Students should be able translate the binary in question 1 to ASCII to get the message "App Inventor ROCKS".
They should, in question 2, be able to explain that JPEG compression is a lossy technique because some information is lost when this technique is used, but that these changes are not perceptible to the human eye and so do not lower the quality of the camera.
Finally, in question 3, they should be able to describe how a binary sequence would be interpreted as a color when used as part an image, as a letter when part of a text message, and so on.
Differentiation: More Practice
To provide more practice with RLE, have students complete these CS Unplugged Worksheets (pg. 17-18). [P3]
Mobile CSP Teachers Michael Wilkosz and Anthony Truss created a Run Length Encoding Image Project in which students recreate their own image using a 16x16 grid in Adobe Illustrator. Alternatively, Paint, Gimp, or PiskelApp.com can be used to complete this assignment.
Mobile CSP Teachers Jessica Breed and Jenn Nelson created a similar Pixel Art Project that involves bringing the images to life using PostITs and posting them around the school building.
Differentiation: Enrichment
To extend students' understanding of RLE have them complete p. 19 of the CS Unplugged Worksheets (pg. 17-18). [P3]
Background Knowledge: Run-Length Encoding
Simple black-and-white images such as fax images, as well as color pictures, have a lot of repetition in them. To reduce amount of the data needed to store and transmit images, computer scientists use a variety of image compression techniques. The technique demonstrated in the video and used in this lesson is known as run-length encoding, or RLE. In this technique, the picture is converted into numbers by recording the length of alternating white and black pixels. This technique is well suited to images that have a lot of repetition in them. For example, fax images often have large blocks of white (e.g. margins) or black pixels (e.g. a horizontal line). Color pictures also have a lot of repetition in them. In practice, programmers choose a compression technique to best suit the image he or she is transmitting.
From CS Unplugged: “If we didn't compress images it would take much longer to transmit pictures and require much more storage space. This would make it unfeasible to send faxes or put photos on a web page. For example, fax images are generally compressed to about a seventh of their original size, so without compression they would take seven times as long to transmit! Photographs and pictures are often compressed to a tenth or even a hundredth of their original size (using a different technique). This allows many more images to be stored on a disk, and it means that viewing them over the web will take a fraction of the time.”
Background Knowledge: Lossy vs Lossless Compression
There are generally two types of image compression techniques. Run-length encoding is a lossless technique, which means that the image is perfectly represented and no data are lost. It is the technique used in TIFF images. It is preferable for medical imaging, archival imaging, clip art, comics, and other applications.
Lossy compression is not perfect. Some data may be lost. JPEG is an example of lossy compression. It is suitable for photographs and other applications where the loss of some data would be imperceptible. The Still Curious section of the Student lesson includes a short presentation on how JPEG works. JPEG compression is based on an algorithm that uses the cosine function. But the presentation leaves out most of the math details. Here is a link to the slides.
The trade-off is between storage required for the image vs. fidelity or quality. If a lot of compression is required -- perhaps because of transmission requirements -- a lossy technique may be preferred.
3.3.2. Professional Development Reflection¶
Discuss the following questions with other teachers in your professional development program.
- How does this lesson help students toward the enduring understanding that all digital data can be represented by a variety of abstractions built upon binary sequences?
- What might be some other trade-offs that students could connect to that would reinforce the enduring understanding that there are trade-offs when representing information as digital data?
- How does this lesson develop students' computational thinking practices, particularly their analysis and problem solving skills and their ability to use abstractions?
-
I am confident I can teach this lesson to my students.
- 1. Strongly Agree
- 2. Agree
- 3. Neutral
- 4. Disagree
- 5. Strongly Disagree