5.8. The Selection Sort¶
The selection sort improves on the bubble sort by making only one exchange for every pass through the list. In order to do this, a selection sort looks for the largest value as it makes a pass and, after completing the pass, places it in the proper location. As with a bubble sort, after the first pass, the largest item is in the correct place. After the second pass, the next largest is in place. This process continues and requires \(n - 1\) passes to sort \(n\) items, since the final item must be in place after the \((n - 1)\)-th pass.
Figure 3 shows the entire sorting process for the selection sort. On each pass, the largest remaining item is selected and then placed in its proper location. The first pass places 93, the second pass places 77, the third places 55, and so on. The function is shown in ActiveCode 1.
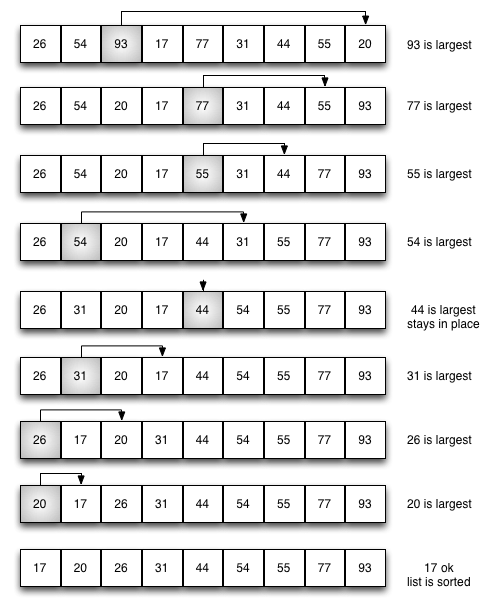
Figure 3: Selection Sort: Complete¶
You may see that the selection sort makes the same number of comparisons as the bubble sort and is therefore also \(O(n^{2})\). However, due to the reduction in the number of exchanges, the selection sort typically executes faster in benchmark studies. In fact, for our list, the bubble sort makes 20 exchanges, while the selection sort makes only 8.
Self Check
- [7, 11, 12, 1, 6, 14, 8, 18, 19, 20]
- Selection sort is similar to bubble sort (which you appear to have done) but uses fewer swaps
- [7, 11, 12, 14, 19, 1, 6, 18, 8, 20]
- This looks like an insertion sort.
- [11, 7, 12, 14, 1, 6, 8, 18, 19, 20]
- This one looks similar to the correct answer but instead of swapping the numbers have been shifted to the left to make room for the correct numbers.
- [11, 7, 12, 14, 8, 1, 6, 18, 19, 20]
- Selection sort improves upon bubble sort by making fewer swaps.
Q-3: Suppose you have the following list of numbers to sort: [11, 7, 12, 14, 19, 1, 6, 18, 8, 20] which list represents the partially sorted list after three complete passes of selection sort?