
6.7. Cryptography Securing the Internet¶
This lesson continues the topic of cryptography, examining cryptographic techniques used to secure data on the Internet. A key concept introduced is that of public and private keys and combining them to ensure secure communication.
Professional Development
The Student Lesson: Complete the activities for Unit 6: Lesson 6.7 Cryptography: Securing the Internet.
Materials
- Slides
- Videos. There are four video clips embedded in this lesson:
- Video 1: CS Unplugged Double-locked box (4:22)
- Video 2: Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange (4:21)
- Video 3: RSA Public Key Encryption (3:59)
- Video 4: Securing the Internet (6:59).
6.7.1. Learning Activities¶
Estimated Length: 45 minutes
- Hook/Motivation (10 minutes): Show Video 1 (4:22), the CS Unplugged video — locking a box with two keys is an analogy for the public key encryption. This video illustrates the key exchange problem. (More info)
- Experiences and Explorations (25 minutes)
- Discussion: Discuss how the key exchange problem, if left unsolved, would make it impossible (or at least very impractical) to have secure transactions on the Internet.
- Presentation 1: Diffie-Hellman: Using the slides or Video 2 (4:21) discuss with
the students the Diffie-Hellman solution to the key exchange problem. The slides and video include a
Brit Cruise video that describes
Diffie-Hellman in terms of a paint-mixing analogy, which nicely illustrates the concept of a
one-way function -- in this case, mixing paint is easy but unmixing it is hard. Emphasize that
Diffie-Hellman uses an intractable mathematical problem (analogous to unmixing paint),
to protect the exchange of a secret key.
Let students experiment with this embedded color-mixing activity, which in addition to illustrating the paint-mixing analogy, also gives them another experience with hexadecimal numbers.
- Discussion: Discuss the color-mixing analogy, emphasizing that Diffie-Hellman uses an intractable mathematical problem (analogous to unmixing paint), to protect the exchange of a secret key.
- Presentation 2: RSA Public Key Encryption: Using the slides or Video 3 (3:59) review RSA and emphasize how it solves the efficiency problem with the Diffie-Helman key exchange.
- Presentation 3: Securing the Internet: Using the slides or Video 4 (6:59) review how the modern cryptographic techniques work together to secure the Internet. Discuss what the 's' in https stands for and how certificates work.
- Rethink, Reflect and/or Revise (10 minutes): Review public key cryptography and the idea that two keys (public and private) should be used. Have students complete the portfolio reflection questions.
AP Classroom
The College Board's AP Classroom provides a question bank and Topic Questions. You may create a formative assessment quiz in AP Classroom, assign the quiz (a set of questions), and then review the results in class to identify and address any student misunderstandings. The following are suggested topic questions that you could assign once students have completed this lesson.
Suggested Topic Questions:
Assessment Opportunities and Solutions
Solutions Note: Solutions are only available to verified educators who have joined the Teaching Mobile CSP Google group/forum in Unit 1.
Differentiation: More Practice
If students are struggling with lesson concepts, have them review the following resources:
Differentiation: Enrichment
Have students bring in a current events article related to cryptography to share with the class.
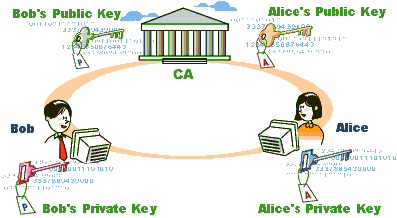
Background Knowledge: Certificate Authorities
This WhatIs.com entry on Certificate Authorities provides a good background on how public keys are issued. The image below might also be helpful in understanding the relationship between the systems.
6.7.2. Professional Development Reflection¶
Discuss the following questions with other teachers in your professional development program.
- How does the lesson reinforce the enduring understanding that cybersecurity is an important concern for the Internet? What other connections or examples would be relevant for students?
-
I am confident I can teach this lesson to my students.
- 1. Strongly Agree
- 2. Agree
- 3. Neutral
- 4. Disagree
- 5. Strongly Disagree