8.6. Call by value¶
When you pass a structure as an argument, remember that the argument and
the parameter are not the same variable. Instead, there are two
variables (one in the caller and one in the callee) that have the same
value, at least initially. For example, when we call printPoint, the stack diagram looks like this:
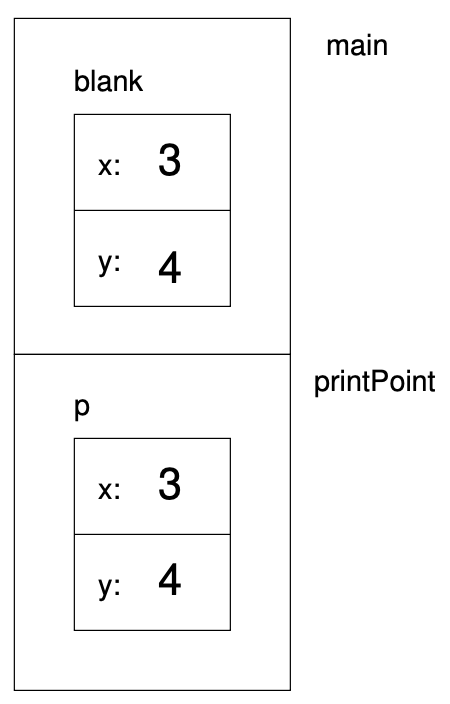
If printPoint happened to change one of the instance variables of
p, it would have no effect on blank. Of course, there is no
reason for printPoint to modify its parameter, so this isolation
between the two functions is appropriate.
This kind of parameter-passing is called “pass by value” because it is the value of the structure (or other type) that gets passed to the function.
Take a look at the active code below. Notice from the output of the code below how the
function addTwo changes the instance variables, but not on blank itself.
2 4-
Take a look at exactly what is being outputted.
2 4 2-
Correct!
4 4 2-
Take a look at exactly what is being outputted.
2 4 4-
Remember the rules of pass by value.
Q-2: What will print?
int addTwo(int x) {
cout << x << " ";
x = x + 2;
cout << x << " ";
return x;
}
int main() {
int num = 2;
addTwo(num);
cout << num << endl;
}
(6, 8), 3-
Correct!
(6, 8), 6-
Remember the rules of pass by value.
(68),3-
Take a look at exactly what is being outputted.
68, 6-
Take a look at exactly what is being outputted.
Q-3: What will print?
struct Point {
int x, y;
};
void timesTwo (Point p) {
p.x = p.x * 2;
p.y = p.y * 2;
cout << "(" << p.x << ", " << p.y << ")";
}
int main() {
Point blank = { 3, 4 };
timesTwo (blank);
cout << ", " << blank.x << endl;
}
Before you keep reading...
Making great stuff takes time and $$. If you appreciate the book you are reading now and want to keep quality materials free for other students please consider a donation to Runestone Academy. We ask that you consider a $10 donation, but if you can give more thats great, if $10 is too much for your budget we would be happy with whatever you can afford as a show of support.