2.6. Strings¶
Strings in Java are objects of the String class that hold sequences of characters (a, b, c, $, etc). Remember that a class (or classification) in Java defines the data that all objects of the class have (the fields) and the behaviors, the things that objects know how to do (the methods).
You can declare a variable to be of type String.
Note
Class names in Java, like String, begin with a capital letter. All primitive types: int, double, and boolean, begin with a lowercase letter. This is one easy way to tell the difference between primitive types and class types.
Run the following code. What does it print?
The code above declares an object variable named greeting and sets the value of greeting to the Java keyword null to show that it doesn’t refer to any object yet. So System.out.println(greeting); will print null.
Object variables refer to objects in memory. A reference is a way to find the actual object, like adding a contact to your phone lets you reach someone without knowing exactly where they are. The value of greeting is null since the string object has not been created yet.

Figure 1: Initial value for an object reference¶
In Java there are two ways to create an object of the String class. You can use the new keyword followed by a space and then the class constructor and then in parentheses you can include values used to initialize the fields of the object. This is the standard way to create a new object of a class in Java.
greeting = new String("Hello");
In Java you can also use just a string literal, which is a set of characters enclosed in double quotes ("), to create a String object.
greeting = "Hello";
In both cases an object of the String class will be created in memory and the value of the variable greeting will be set to an object reference, a way to find that object.
Here is an active code sample that creates two greeting strings: one using a string literal and the other using new and the String constructor. Change the code to add 2 new strings called firstName and lastName, one using a string literal and the other using new, and print them out with the greetings.
Now that greeting refers to an actual object we can ask the object what class created it. Try the following. What does it print?
The code above will first print class java.lang.String since greeting was created by the String class. The full name for the String class is java.lang.String. The java.lang part is the package name. Every class in the Java language is in a package and the standard classes like String are in the java.lang package. Every object in Java knows the class that created it. Also, every class knows its parent class. Yes, a class can have a parent class, just as people have parents. But, in Java a class can only have one parent. A class can inherit object fields and methods from a parent class, just like you might inherit musical ability from a parent. The fourth line will print class java.lang.Object because the parent class (superclass) of the String class is the Object class. All classes in Java inherit from the Object class at some point in their ancestry.
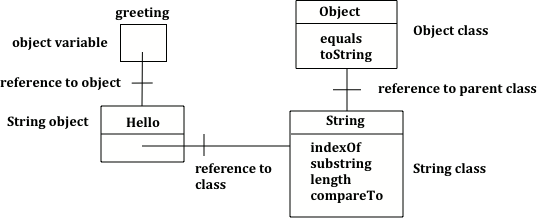
Figure 2: Object variable of type String with a reference to a String object which has a reference to the String class which has a reference to the Object class.¶
2.6.1. String Operators - Concatenation¶
Strings can be appended to each other to create a new string using the + or += operator . This is also called concatenation.
Try the following code. Add another variable lastName that is “Hernandez”. Use += or + to add the lastname variable after name to the result, with a space between first and last name. Add 2 more exclamation points (!) to the end of the happy birthday greeting in result.
Note
Note that spaces are not added between strings automatically. If you want a space between two strings then add one using + “ “ +. If you forget to add spaces, you will get smushed output like “HiJose” instead of “Hi Jose”. And remember that variables are never put inside the quotes (“”) since this would print the variable name out letter by letter instead of its value.
- xyz
- s1 will equal "xy" plus another "xy" then z at the end.
- xyxyz
- s1 contains the original value, plus itself, plus "z"
- xy xy z
- No spaces are added during concatenation.
- xy z
- No spaces are added during concatenation, and an additional "xy" should be included at the beginning.
- z
- s1 was set to "xy" initially, so the final answer will be "xyxyz"
2-6-5: Given the following code segment, what is in the string referenced by s1?
String s1 = "xy";
String s2 = s1;
s1 = s1 + s2 + "z";
You can even add other items to a string using the + operator. The other item will be converted to a string using the toString operator if it is an object and then appended to the current string. All objects inherit a toString method that returns a string representation of the object.
What do you think the following will print? Guess before you hit run. If you want the addition to take place before the numbers are turned into a string what should you do? Try to modify the code so that it adds 4 + 3 before appending the value to the string. Hint: you used this to do addition before multiplication in arithmetic expressions.
Note
If you are appending a number to a string it will be converted to a string first before being appended.
Since the same operators are processed from left to right this will print 1243. First 4 will be turned into a string and appended to 12 and then 3 will be turned into a string and appended to 124. If you want to do addition instead, try using parentheses!
What if you wanted to print out a double quote “ character? Since the double quote “ is a special character with meaning in Java, we put in a backslash in front of the quote to signal that we want just the character. This is called a backslash escape sequence. And if you wanted to print out a backslash, you would have to backslash it too in order to escape its special meaning. Another useful backslashed character is backslash \n which will put in a newline.
2.6.2.  Programming Challenge : Mad Libs¶
Programming Challenge : Mad Libs¶
Have you ever played MAD LIBS? In this game, you first choose a bunch of words without looking at the story and then those words are filled into the story to make it sound very wacky! Fill in the variables below with Strings for each word, and then run to see the wacky story.
Then, come up with another story that uses at least 5 new String variables. When you’re done, try another team’s mad libs code. If you create this program in a Java IDE, you can use input to read in the words (see input examples using the Scanner class).
If you used repl.it for this challenge, copy the url of your repl here to turn in.
2.6.3. Summary¶
Strings in Java are objects of the
Stringclass that hold sequences of characters.String objects can be created by using string literals (String s = “hi”;) or by calling the String class constructor (String t = new String(“bye”);).
new is used to create a new object of a class.
null is used to indicate that an object reference doesn’t refer to any object yet.
String objects can be concatenated using the + or += operator, resulting in a new String object.
Primitive values can be concatenated with a String object. This causes implicit conversion of the values to String objects.
Escape sequences start with a backslash \ and have special meaning in Java. Escape sequences used in this course include ", \, and \n to print out a quote, backslash, and a new line.

