This book is now obsolete Please use CSAwesome instead.
9.1. Lists¶
When you go shopping, you might create a list. As you shop you might check things off your list (remove them from the list). You might search your list to see if something is already on it. You might add to a list. A list holds items in an order.

Figure 1: A couple of lists¶
9.2. The List Interface¶
Java uses the notion of a list too. It defines the interface List which is in the java.util package. An interface lets you define a type based on what you want it to do, not how it does it. Several classes can implement the same interface and you can pick the one to use that works best in your situation.
See http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/List.html for the Java documentation for the List interface (a portion of this is shown below). All classes in the Java language are organized into packages. A package contains related classes. The String and Object classes are in the java.lang package. The full name for any class is the package name followed by a . and the class name. So the full name for the String class is java.lang.String. The full name for the List interface is java.util.List.
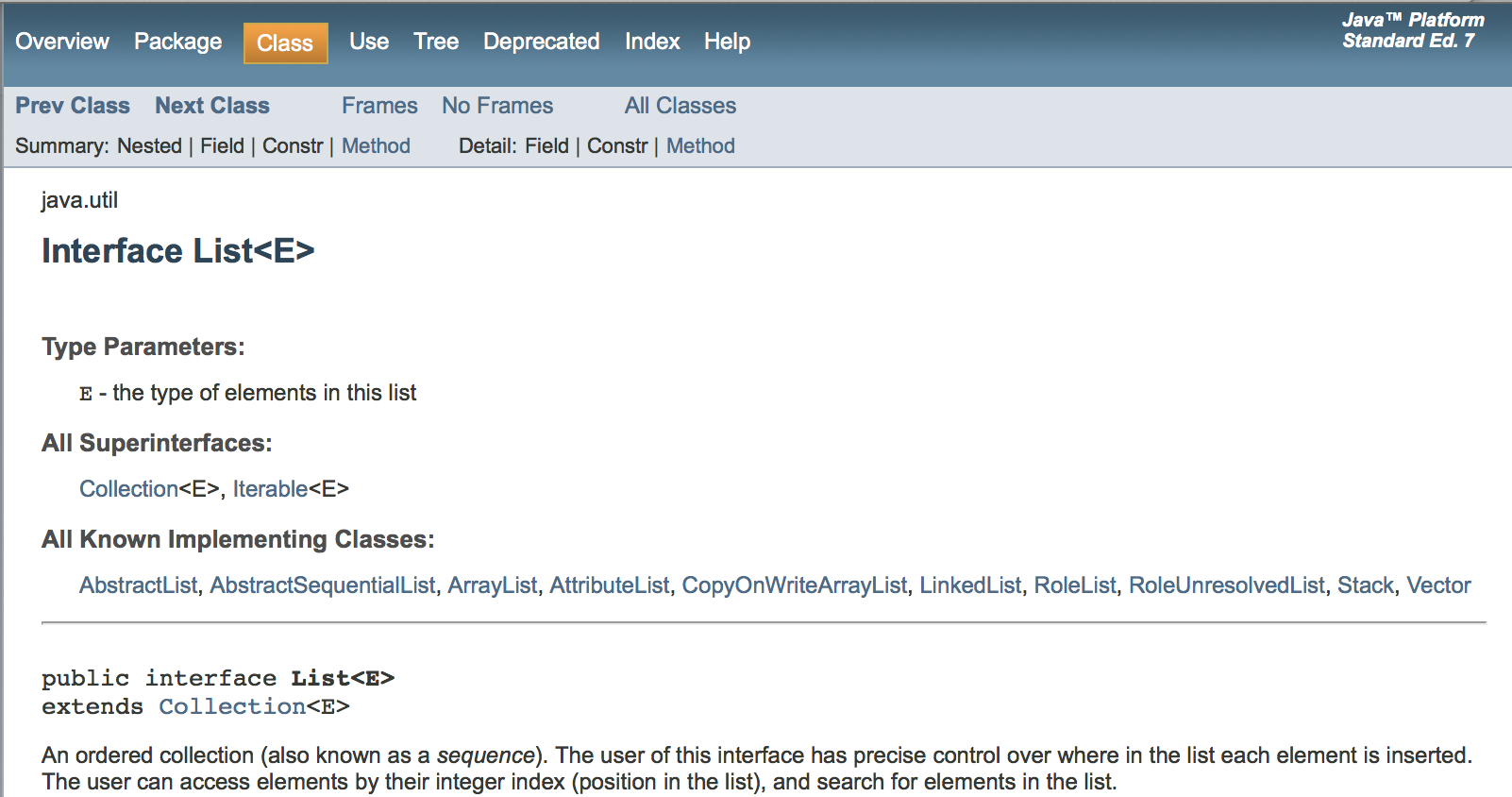
Figure 2: The List interface in Java¶
